What is P&SC?
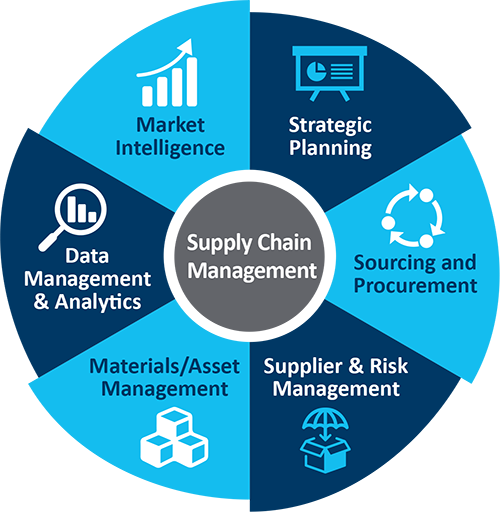
Procurement and supply chain management are closely related fields that involve the acquisition and management of goods, services, and materials.
Procurement management is the process of acquiring goods, services, or works from an external source. It involves identifying needs, specifying requirements, selecting suppliers, negotiating contracts, and managing the acquisition and delivery of the goods or services.
Supply chain management, on the other hand, is the coordination and management of all activities involved in the production and delivery of a product or service. It includes procurement, but also encompasses other activities such as planning, logistics, and production. Supply chain management aims to optimize the flow of materials, information, and finances through the entire supply chain, with the goal of delivering products or services to customers in the most efficient and cost-effective manner possible.
In summary, Procurement management is a subset of Supply chain management, Procurement is responsible for acquiring goods and services while Supply chain management oversee the entire flow of materials, information, and finances through the entire supply chain, including procurement.
Procurement and supply chain management are fields that draw from several different sciences, including economics, operations research, industrial engineering, logistics, and management science.
Economics provides the framework for understanding how markets work, and how firms and individuals make decisions about the allocation of resources. Procurement management and supply chain management both involve decisions about how to allocate resources such as money, time, and materials in the most efficient way possible.
Operations research and industrial engineering are used to optimize and model different aspects of procurement and supply chain management. For example, operations research techniques such as linear programming and queuing theory can be used to optimize production schedules and logistics networks.
Logistics is the science of planning and executing the movement of goods and materials, which is a critical aspect of supply chain management. Logistics management deals with the flow of materials, information, and finances through the entire supply chain.
Finally, management science provides the tools and frameworks for making decisions and managing organizations, which are essential for effective procurement and supply chain management. This includes decision-making tools such as cost-benefit analysis and risk management, as well as frameworks for organizing and structuring procurement and supply chain management processes.
In short, procurement and supply chain management are interdisciplinary fields that draw from a variety of sciences to help organizations effectively acquire and manage the goods and services they need to operate.
Areas of Procurement and Supply Chain Management
Procurement and supply chain management encompass a wide range of areas and activities, including:
- Strategic sourcing:
- Contract management
- Category management
- Logistics and distribution
- Demand management
- Supply chain planning
- Performance management
- Procurement technology
- International procurement and supply chain management
- Sustainability and responsible procurement
These are some of the main areas of procurement and supply chain management, but depending on the organization and the specific role, the focus may be different.
Research Methods
Procurement and supply chain management research can be conducted using a variety of methods. Some common research methods used in these fields include:
Surveys: Surveys can be used to gather information from a large number of individuals or organizations. Surveys can be conducted through mail, phone, email, or online, and can be used to gather data on a wide range of topics, such as procurement practices, supplier selection criteria, and supply chain performance.
Case Studies: Case studies involve the in-depth examination of a specific organization or situation. Case studies can be used to gain a deeper understanding of procurement and supply chain management practices in a particular industry or context.
Experiments: Experiments can be used to test specific hypotheses or theories related to procurement and supply chain management. Experiments can be conducted in a laboratory or in a field setting, and can involve manipulating different variables to study their impact on procurement and supply chain outcomes.
Simulation: Computer simulations can be used to model and analyze different procurement and supply chain scenarios. This approach can be used to study the impact of different decisions and policies on procurement and supply chain performance.
Field Research: Field research can be used to conduct observational or participatory research in a natural setting. Field research can be used to study procurement and supply chain practices in a real-world context, and can involve observing or interviewing individuals or organizations.
These are some common methods used in procurement and supply chain management research, but it’s important to note that depending on the research question or hypothesis, different methods may be more appropriate to use.
Practice
Practitioners of Procurement and Supply Chain Management typically work in the following ways:
Practitioners of procurement and supply chain management typically work in a variety of ways to ensure that an organization has the goods and services it needs to operate effectively. Some common tasks and responsibilities of procurement and supply chain management practitioners include:
Identifying and specifying requirements: Practitioners work with internal stakeholders to identify the goods and services that an organization needs, and to specify the requirements for those goods and services.
Sourcing and selecting suppliers: Practitioners are responsible for identifying potential suppliers, evaluating their capabilities, and selecting the most appropriate suppliers for an organization.
Negotiating contracts: Practitioners work with suppliers to negotiate the terms and conditions of contracts, including prices, delivery schedules, and quality standards.
Managing the procurement process: Practitioners are responsible for managing the entire procurement process, from identifying needs to delivery of the goods or services.
Managing supplier relationships: Practitioners work to maintain positive relationships with suppliers, and to manage any issues that may arise.
Managing logistics and distribution: Practitioners work to ensure that goods and services are delivered to the organization in a timely and cost-effective manner.
Managing inventory and stock levels: Practitioners work to ensure that inventory and stock levels are managed in a way that meets the organization’s needs.
Analyzing data and identifying trends: Practitioners use data analysis to identify trends and patterns in procurement and supply chain activities, and to make informed decisions.
Risk management: Practitioners work to identify and mitigate risks that could affect procurement and supply chain activities.
Continuous improvement: Practitioners work to continuously improve procurement and supply chain processes and performance through the implementation of best practices and new technologies.
These are some common tasks and responsibilities of procurement and supply chain management practitioners, but depending on the organization, and their specific role, they may have different responsibilities and duties.
